Graves’ Eye Disease
Graves' Eye Disease, also known as Thyroid Eye Disease, is a significant, yet often overlooked, manifestation of thyroid dysfunction. This autoimmune condition primarily affects individuals with an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, caused by Graves' disease.
Its hallmark symptoms, such as eye bulging, discomfort, and vision changes, can be distressing and affect one's quality of life. Understanding the link between thyroid health and eye symptoms is crucial for effective management and maintaining overall well-being.
This blog explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Graves' Eye Disease, providing essential knowledge to help those affected navigate this challenging condition.
What is Graves’ Eye Disease?
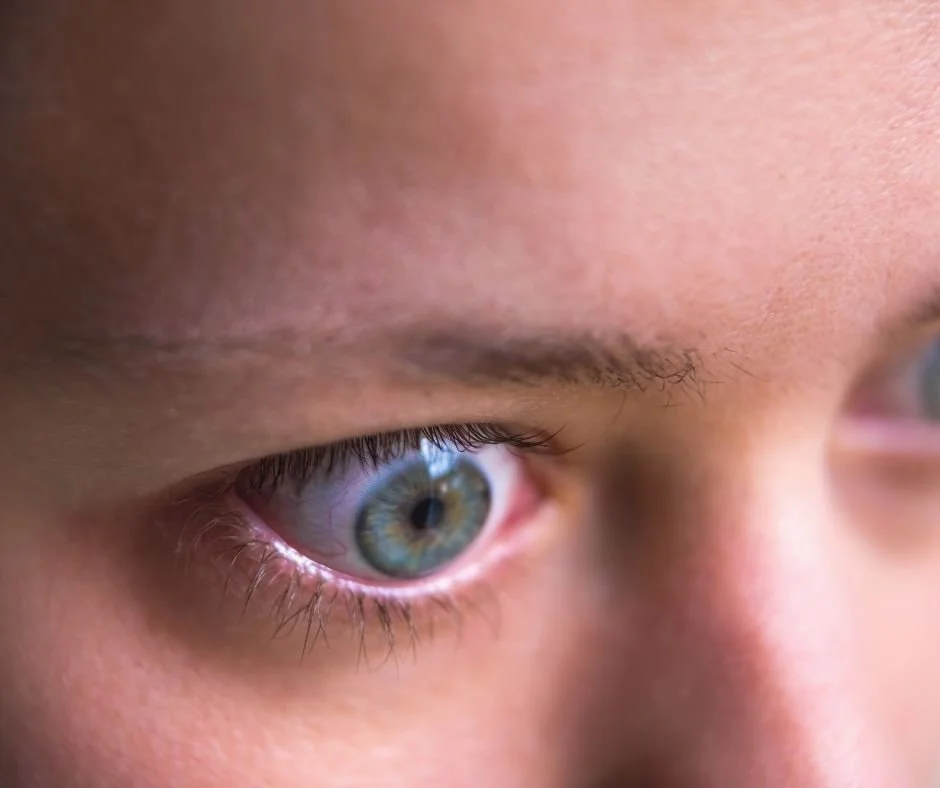
Graves' Eye Disease is an autoimmune disorder that results in inflammation and other symptoms in the eyes.
It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland and, frequently, the tissues around the eyes. This attack causes swelling that can lead to noticeable bulging of the eyes, a hallmark sign of the condition.
It's closely linked to Graves' disease, a form of hyperthyroidism, but it can occasionally occur in individuals with normal thyroid function or even hypothyroidism.
Causes of Graves’ Eye Disease
The exact cause of Graves' Eye Disease is not fully understood but it is known to be primarily associated with an immune system dysfunction. The immune system produces antibodies that mistakenly target the tissue around the eyes, causing inflammation and an accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (substances that attract more water into the tissues, causing swelling).
Risk factors include smoking, genetic predisposition, and hormonal factors.
Symptoms and Early Signs
The symptoms of Graves' Eye Disease can vary widely but typically include:
Eye Bulging (proptosis)
One of the most noticeable signs that can be visually disturbing.
Redness and Swelling
Often occurs around the eyes and eyelids.
Dry or Watery Eyes
Changes in tear production can cause discomfort.
Sensitivity to Light and Visual Blurriness
These symptoms can impair daily activities.
Double Vision or Vision Loss
In severe cases, the optic nerve may be compressed causing double vision and/or vision loss.
Grave’s Eye Disease symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning and emotional well-being, making early recognition and treatment essential.
Diagnosing Graves' Eye Disease
Diagnosing Graves' Eye Disease typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by both an endocrinologist and an ophthalmologist.
Diagnostic tests may include:
Clinical examination
Assessing eye appearance and function.
Imaging tests
MRI or CT scans to view the extent of eye involvement.
Blood tests
Checking levels of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment for Graves' Eye Disease focuses on managing symptoms and addressing the underlying thyroid imbalance.
Treatment options include:
Medications
Corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce inflammation, or immunosuppressants in severe cases.
Surgery
For severe cases, orbital decompression surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the eye muscles and optic nerve.
Radiotherapy
Used sparingly, to reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle modifications
Including quitting smoking and using protective eyewear.
Living with Graves' Eye Disease
Living with Graves' Eye Disease presents unique challenges. The visible symptoms can affect self-esteem and social interactions, while the physical symptoms can impact professional activities and personal hobbies.
Support from healthcare providers, coupled with an informed and supportive community, is essential. Managing stress, prioritizing eye health, and regular follow-ups are key to improving quality of life.
Prevention and Monitoring
While Graves' Eye Disease cannot always be prevented, monitoring thyroid health and managing Graves' disease effectively can help minimize the severity of eye symptoms. Regular thyroid function tests and eye exams are crucial for those at risk or already diagnosed with thyroid disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions about Graves' Eye Disease
Q: What causes Graves' Eye Disease?
A: Graves' Eye Disease is primarily caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the tissues around the eyes. This is often associated with thyroid dysfunction, specifically hyperthyroidism caused by Graves' disease.
Q: Can Graves' Eye Disease lead to blindness?
A: While severe cases of Graves' Eye Disease can potentially threaten vision due to pressure on the optic nerve, blindness is rare. Timely and effective treatment can greatly reduce the risk of serious complications.
Q: Is smoking linked to Graves' Eye Disease?
A: Yes, smoking is a significant risk factor for developing Graves' Eye Disease and can exacerbate the severity of the symptoms. Quitting smoking is strongly recommended to help manage the condition.
Q: How is Graves' Eye Disease treated?
A: Treatment varies depending on the severity but may include medications to reduce inflammation, corrective surgery, or radiotherapy to target inflamed tissues. Managing underlying thyroid levels is also crucial.
Q: Can children get Graves' Eye Disease?
A: Graves' Eye Disease primarily affects adults, but children and teenagers who develop Graves' disease can also develop this eye condition. Paediatric cases require careful management by a paediatric endocrinologist and ophthalmologist.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Graves' Eye Disease?
A: Beyond quitting smoking, protecting eyes from wind and sun, using lubricating eye drops, wearing sunglasses, and elevating the head during sleep can help alleviate symptoms.
Q: What is the prognosis for someone with Graves' Eye Disease?
A: The prognosis for patients with Graves' Eye Disease generally is good, especially with early diagnosis and treatment. Most patients can manage symptoms effectively with proper treatment and can maintain a good quality of life.
Conclusion
Graves' Eye Disease is a complex condition with significant implications for those affected. Through early detection, appropriate treatment, and comprehensive management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite this challenging condition. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Graves' Eye Disease, prompt action and consultation with healthcare professionals are crucial, so make sure your eyes get the love they deserve!